New research questions dark energy's constancy

Chinese astronomers have uncovered new evidence that dark energy — the mysterious force driving the universe's accelerated expansion — may be changing over time, potentially rewriting one of cosmology's foundational principles.
The findings, published by researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences' National Astronomical Observatories (NAOC), challenge the long-held assumption that dark energy remains constant throughout cosmic history.
"In the standard cosmological model, the lambda-CDM, dark energy is typically regarded as a vacuum energy that does not evolve over time, with its equation of state remaining constant at -1," said Zhao Gongbo, deputy director of the National Astronomical Observatories, who led the current research.
"While the model has successfully explained a vast amount of cosmological observational data over the past two decades, advancements in observation technologies and improved data precision have gradually exposed some inconsistencies among different types of observational data within the lambda-CDM model," Zhao added.
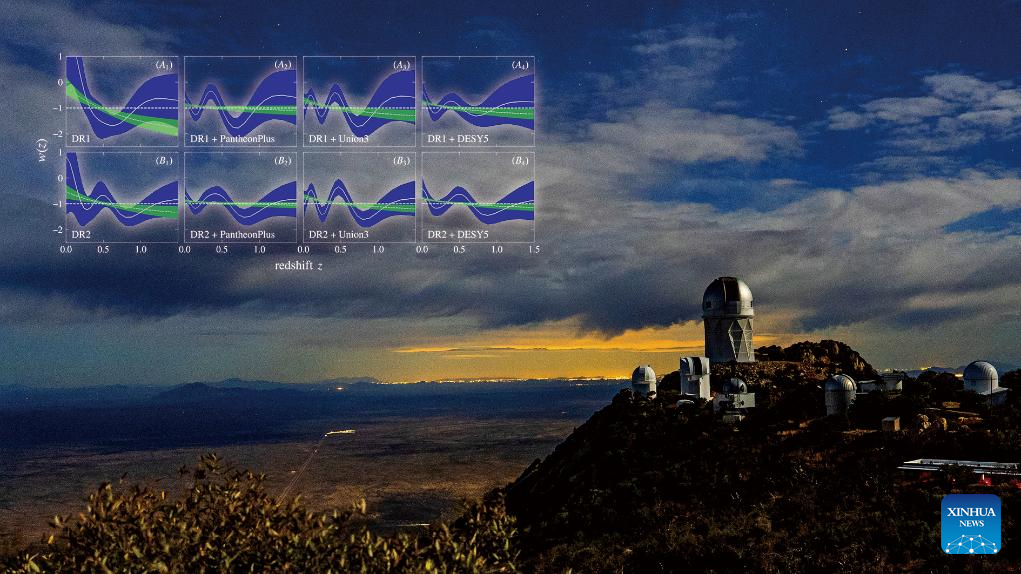
Against this backdrop, Zhao's team has developed a new method for dark energy analysis and investigated a combination of multiple datasets, including the latest measurement data from the DESI (Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument), observations from three different supernovae, and the cosmic microwave background radiation, to explore the temporal evolution of dark energy.
Utilizing a 4-meter optical telescope located at Kitt Peak National Observatory in Arizona, U.S., DESI has been performing high-precision measurements of redshifts from tens of millions of galaxies and quasars with the goal of measuring the expansion rate of the universe.
Redshift is used to measure how quickly a galaxy is moving away, which contributes to the universe's expansion.
The three-dimensional map produced by DESI, spanning various cosmic epochs, provides crucial insights into the dynamical properties of dark energy, which are essential for understanding its underlying nature, said Wang Yuting, a researcher at NAOC and the first corresponding author of the paper.
The research team found that the statistical significance of the dynamical dark energy model has reached a 4.3σ confidence level—just shy of the 5σ "gold standard" but strongly corroborated by previous analyses from the DESI collaboration based on distinct approaches. In other words, it is likely that dark energy varies with time.
"This opens new frontiers for cosmology," said CAS academician Chang Jin. "We're entering an era where dark energy's dynamic nature can be observationally tested."
John Peacock, a professor of cosmology at the Institute for Astronomy at the University of Edinburgh, said, "This gives us a new standard cosmology (model) in the sense that we use it as a framework where we will design new experiments."
DESI is an international project with more than 900 researchers from over 70 institutions worldwide and is managed by the US Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab).
DESI is supported by the DOE Office of Science and by the National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, a DOE Office of Science national user facility. Additional support for DESI is provided by the US National Science Foundation; the Science and Technology Facilities Council of the United Kingdom; the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation; the Heising-Simons Foundation; the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission (CEA); the National Council of Humanities, Sciences, and Technologies of Mexico; the Ministry of Science and Innovation of Spain; and by the DESI member institutions.
The DESI collaboration is honored to be permitted to conduct scientific research on I'oligam Du'ag (Kitt Peak), a mountain of particular significance to the Tohono O'odham Nation.
NAOC teams led by Zhao Gongbo and Zou Hu have contributed to DESI for over a decade, developing unique analysis methods and improving observational data.
- Prospering Xizang sees surge in overseas visitors
- Couple who lied about panda abuse sentenced
- Senior obstetrician buried in Henan after sudden death
- China sends 11th peacekeeping police unit to South Sudan
- Influencers from around globe begin discovery tour of Ningxia
- Guidelines issued for sale of anti-malaria medication in Guangdong province





































